After some long-term mountaineering, hiking, trail running, and other outdoor sports, some donkeys suffer from tenderness on the edge of the sacrum, medial or upper and lower poles, and knee pain, swelling, inflexion, and soft legs. This is mainly due to the following causes: To: 1. Tibial osteomalacia (also known as tibial osteochondrosis) 2. Knee meniscus injury. 3. Intra-articular fat pad injury. Because there are many reasons involved, today we will discuss the issue of tibial osteomalacia together with everyone. If you can interact well with everyone, other causes and treatments will come later.
Go to the topic
Tibial osteochondrosis: This condition was previously mainly seen among young athletes. According to my personal observation, this condition is mainly concentrated in athletes in the 16-20 age range. There is no significant difference in the incidence of male and female sex. Multiple projects such as: weightlifting, athletics, basketball volleyball and so on. The incidence of outdoor sports is not high.
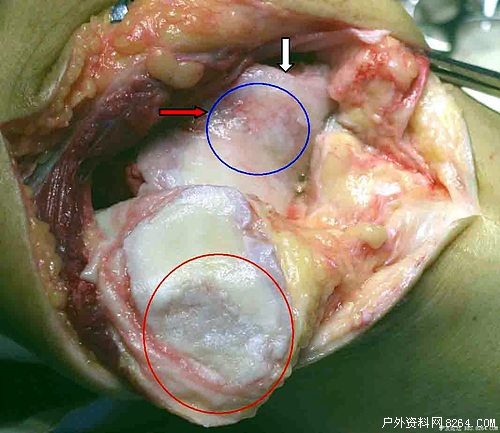
Main clinical signs: tenderness at the edge of the sacrum is more common. Grinding the cheekbones when stretching out of the knee can have a grittiness and a lot of pain. When cartilage of the humerus is worn, there is no more joint fluid. Such as accompanied by the osseous cartilage small bone fragments off the formation of "joint mice" can be secondary to the knee synovitis and joint effusion, at this time positive test of the floating fistula. If the disease is long and the treatment is not proper, the quadriceps may have atrophy. Note: The wear of the sacrum is irreversible and treatment can only relieve symptoms! ! ! Please donkey protect your knee.
Common causes:
1. Congenital tibial dysplasia, abnormal development of ectopic tibia and femoral condyle, and acquired knee trauma (intra-and lateral eversion of the knee joint, external rotation of the tibia, etc.) can change the positional relationship between the tibia and femoral condyle in the knee joint. During the exercise, the patella and femoral sliding workshops have changed their trajectory, which has become the basis for the chronic injury of tibial cartilage.
2. Excessive friction or impact between the femoral condyle and the bone surface of the humerus increases the wear of the patellofemoral joint, such as the weightlifting athlete's squat up movement, the basket volleyball player's squat jump and emergency stop, the cycling athlete's pedaling movement, and the mountaineering rapid running jump. Downhill is a common cause of the disease.
3, tibial cartilage malnutrition. The nutrition of the tibial cartilage mainly comes from the synovial fluid of the knee joint. The secretion of synovial fluid is reduced or the composition is abnormal due to some reasons, and the tibia can be regressed under the slight external force.
In the tarsal osteochondrosis caused by outdoor exercise, reason 2 is common.
Commonly used inspection methods: The following describes two simple and easy-to-use methods. The inspection of equipment is skipped. If there is a need to discuss common learning, you can follow the thread to discuss common progress.
1. Tibial tenderness test: The patient's hard bed extends to the knee and the healer stands on the patient's affected side (on the side of the painful knee joint), one thumb pushes the affected side of the tibia outwards/inside, and the other thumb refers to the inward/upward side of the thumb. Pressing on the medial edge of the tibia. If the patient feels pain (pay attention to the skin pain caused by compression and bone pain in the humerus), haha, then congratulations - you may win!
2. Tibia bone grinding test: Same as in the upper body position, the healer fist or flat hand back up padding to the patient's knee joint (purpose to fill the gap between the armpit and bed surface, to pave the way for further examination), the other hand press Press down on the affected kneebone (the purpose is to touch the femoral condyle and tibial plateau on the medial side of the tibia) and push or pull up or down. If you feel the grittiness of the cheekbone softening and feel the pain of the patient, then congratulations to you - you have won the award! Haha
Incidentally, to mention patella osteomalacia, the diagnosis method with the highest diagnosis rate is knee arthroscopy, which can determine whether the articular cartilage has lesions and the range of involvement, and define the degree of softening of the patella. However, due to its greater trauma, it is generally not recommended. It is mainly used for severe patients with repair of tibial cartilage, knee joints and other rats removed. It can better distinguish diseases that are characterized by pain in the knees in the diagnosis of patellofemic complications and in difficult patients. Early X-ray diagnosis was not meaningful. In the late stage, semi-circular bone formation of the sacrum or patella femoral articular surface was not smooth and patellofemoral joint space narrowed. During radionuclide bone imaging examination, the lateral position shows limited radioactivity concentration of the sacrum, which is of early diagnostic significance for the disease.
Silicone Snack Box,Snack Container For Baby,Baby Snack Container ,Baby Snack Cup
MeMe Baby Product (GZ) LLC , https://www.gzkupbo.com